|

|
|

1/2 /3-4/
5-9/Aa-Am/An-Az/B/Ca-Ce/Cf-Cz/Da-Dh/Di-Dz/E/F/G/H/I/J/K/L/M/N/O/Pa-Pf/
/Pj-Po/Pp-Pz/Q/R/Sa-Ss/St-y/Ta-Th/Ti-Tz/U/V/W/X/Y/Z
/ Chinese spelling
|
|
|
|
offer you
better services |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
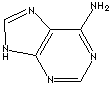
ADENINE
|
| PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION |
| CAS
NO. |
73-24-5
(Base) |
|
| 2922-28-3
(HCl), 321-30-2 (Sulfate) |
| EINECS
NO. |
200-796-1 |
| FORMULA |
C5H5N5 |
| MOL
WT. |
135.13 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2933.59 |
| TOXICITY |
Oral
rat LD50: 227 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Vitamin
B4; 6-Aminopurine; |
| 1H-Purin-6-amine;
Ade; Adenin; Adeninimine; 1,6-Dihydro-6-iminopurine; 3,6-Dihydro-6-iminopurine;
6-Amino-1H-purine; 6-Amino-3H-purine; 6-Amino-9H-purine; 6-Amino-7H-purine;
1,6-dihydro-6-imino-9H-Purine; 9H-Purin-6-yl-amin; 9H-Purine-6-amine; |
| DERIVATION |
|
| CLASSIFICATION |
|
| PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
360 -
365 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
slightly
soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
| Purine
is a heterocyclic compound featured by a fused pyrimidine and
imidazole rings composed of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The simplest
one is purine itself and the two major purines are adenine(6-Aminopurine)
and guanine(2-Amino-6-hydroxypurine). Other important purines
are caffeine, uric acid, theobromine, and theophylline. Purine
and its derivatives are biologically important components of
nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| ADENINE
BASE |
| APPEARANCE |
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
| ASSAY |
99.0%
min |
| HEAVY
METALS |
10ppm
max |
| RESIDUE
ON IGNITION |
0.1%
max |
| LOSS
ON DRYING |
0.5%
max |
| ADENINE
HCl |
| APPEARANCE |
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
| ASSAY |
99.0%
min |
| HEAVY
METALS |
10ppm
max |
| RESIDUE
ON IGNITION |
0.1%
max |
| LOSS
ON DRYING |
5.2%
max |
| ADENINE
SULFATE |
| APPEARANCE |
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
| ASSAY |
99.0%
min |
| HEAVY
METALS |
10ppm
max |
| RESIDUE
ON IGNITION |
0.1%
max |
| LOSS
ON DRYING |
9.0%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
20kgs
in fiber drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| European
Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: 22-26-36 |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF NUCLEOSIDE |
| Ribose
is a pentose (five-carbon sugar) that is a component of the
ribonucleic acid (RNA), where it alternates with phosphate groups
to form the 'back-bone' of the RNA polymer and binds to nitrogenous
bases. Ribose phosphates are components of the nucleotide coenzymes
and are utilized by microorganisms in the synthesis of the amino
acid histidine. Its close relative, deoxyribose, is a constituent
of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), where it alternates with phosphate
groups to form the 'back-bone' of the DNA polymer and binds
to nitrogenous bases. The presence of deoxyribose instead of
ribose is one difference between DNA and RNA. Ribose has one
more oxygen atom in its molecule than deoxyribose. Ribose has
a five member ring composed of four carbon atoms and one oxygen.
Hydroxyl groups are attached to three of the carbons. The other
carbon and a hydroxyl group are attached to one of the carbon
atoms adjacent to the oxygen. In dexoyribose, the carbon furthest
from the attached carbon is stripped of the oxygen atom in what
would be a hydroxyl group in ribose. The sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
molecules in the nucleic acid are all oriented in the same direction.
Their carbon atoms are numbered: the 5' carbon atom is always
on the side of the sugar molecule that faces the leading end,
while the 3' carbon atom always faces the tail end. Nucleotide
is the structural unit of a nucleic acid. A nucleotide consists
of either a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine)
, a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and a phosphate group
attached at the 5' position on the sugar. A nucleoside consists
of only a pentose sugar linked to a purine or pyrimidine base,
without a phosphate group. Purine bases are Adenine, Guanine
and Hypoxanthine (examples of purine nucleosides are Adenosine,
2'-Deoxyadenosine, Guanosine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine, Inosine, 2'-Deoxyinosine).
Pyrimidine bases are Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil (examples
of pyrimidine nucleosides are Cytidine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine, 5-Methyluridine,
2'-Deoxy-5-Methyluridine, Uridine, 2'-Deoxyuridine). The nucleoside
derivatives are involved in important functions in cellular
metabolism and are used to synthesize enzyme inhibitors, antiviral
agents, and anticancer agents. |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
This data is only for your information purposes and does not imply
guarantee for a certain application. |
|
|
| |
If you need
an indicative price to your country, please kindly advise the annual
quantity needed, destination port and we will send you our soonest
CNF(Cost + Freight) price. Your indication for a workable price
level will sure speed up our fastest service for you |
|
|
| |
We really need to get
feed back from our customers in order to improve our performances.
Any information about quotations from competitors will be welcomed
since we hope to work as a team with you.
Your kind help will be very much appreciated.
Best regards from SHENZHEN
, China
Mr. JEFFERY TSUI
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Material
Safety Data Sheet |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
 |
|
|
| |
If the above information
doesn't cover |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
