![]()
![]()
1/2 /3-4/ 5-9/Aa-Am/An-Az/B/Ca-Ce/Cf-Cz/Da-Dh/Di-Dz/E/F/G/H/I/J/K/L/M/N/O/Pa-Pf/ /Pj-Po/Pp-Pz/Q/R/Sa-Ss/St-y/Ta-Th/Ti-Tz/U/V/W/X/Y/Z / Chinese spelling
|
|
|
offer you better
services
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Paclitaxel |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DESCRIPTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Paclitaxel is a natural
product with antitumor activity. Natural Paclitaxel is extracted from
Taxus chinensis and purified by HPLC method without any semi-synthesis
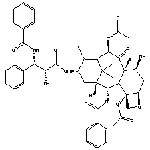
process. The chemical name for paclitaxel is (2aR,4S,4aS,6R,9S,11S,12S, 12aR,12bS)-1,2a,3,4,4a,6,9, 10,11,12,12a,12b-Dodecahydro- 4,6,9,11,12,-12b-hexahydroxy- 4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl- 7,11-methano-5H-cyclodeca [3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-5-one 6,12b-diacetate,12-benzoate, 9-ester with (2R,3S)-N-benzoyl-3- phenylisoserine. Paclitaxel is a white to off-white crystalline powder and is highly lipophilic, insoluble in water, and melts at around 216-217°C. It has a molecular weight of 853.93 and a molecular formula C47H51NO14 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS:33069-62-4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paclitaxil Injections | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paclitaxil water soluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Docetaxel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10-DABIII | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cephalomannine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Please note the Specification Data of Paclitaxel in the following table. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The
high quality of Natural Paclitaxel has been monitored thoroughly
according the FDA (USA) and the Department of Health (China) Standards.
F.W. : 853.93 Assay (HPLC) : > 99.5% IR Spectrum : Identical to Standard. MASS Spectrum : Identical to Standard. NMR Spectrum : Identical to Standard. UV Spectrum (0.002% methanol solution) : Maximum absorption at 227 (+/_2) nm.. Specific Rotation : 49O (+/_ 0.5). Melting Point : 213 - 217OC (with decomposition). Moisture (K.F.) : < 1.5% Impurities (7-epi-10-deacetyl taxol) (HPLC) : < 0.5%. Total Impurities (HPLC) : < 0.5% Residue on Ignition (USP 23 method) : < 0.2% Heavy Metals (USP 23 method II) : < 20 ppm Chlorides : < 0.1% Description : White microcrystalline powder. Solubility : Practically incoluble in water. Easily soluble in methanol, chloroform and ethyl ether. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS NAME OF PRODUCT: PACLITAXEL BATCH NO.: 991229 REPORT DATE: DEC 29,1999 QUANTITY: SAMPLE
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nature
has provided many excellent medicines to benefit the human health.
There are many effective anti-cancer agents in current use originally
came from nature.
Paclitaxel may be one of the most important anticancer agents to be developed over the pasttwo decades. With its unique mechanism of action as an inducer of tubulin assembly,paclitaxel has demonstrated impressive antitumor activity in patients with breast, lung (both non-small cell and small cell), head and neck, and advanced and platinum-refractory ovarian carcinomas. Paclitaxel's antitumor activity was discovered in the 1960s during a largescale 35,000 plants-screening program sponsored by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), USA. In 1983, NCI
began conducting clinical trials of paclitaxel's safety and its
effectiveness against various types of cancer. Demand for paclitaxel
increased in 1989 after the investigators at The Johns Hopkins Oncology
Center reported that the drug produced partial or complete responses
(shrinking or disappearance of the tumor) in 30 percent of previously
treatedpatients with advanced ovarian cancer. it was clear that
ovarian cancer patients with few otheroptions benefited from the
treatment. In December 1992, FDA approved the use of paclitaxel for refractory (treatment-resistant) ovarian cancer Subsequently, clinical trials using paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced breast cancer demonstrated that the drug is effective against this disease. In April 1994, FDA approved the use of paclitaxel for breast cancer that has recurred within 6 months after the completion of initial chemotherapy and for metastatic breast cancer that is not responding to combination chemotherapy. March 1997, FDA designated TaxolÒ (Paclitaxel Injection) as Orphan Drug for treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. April 1998, FDA gave an additional approval for Paclitaxel injections, for first-line therapy for the treatment of advanced carcinoma of the ovary in combination with cisplatin. June 1998, Bristol-Myers
Squibs Company (BMS) received an NDA 20-262/S-024 for a TaxolÒ
indication: in combination with cisplatin, for the first-line treatment
of non-small cell lung cancer in patients who are not candidates
for potentially curative surgery and/or radiation therapy To date, 180
clinical trials have been conducted, researchers have found the
drug to be active in lung, head and neck, bladder, esophageal, and
germ cell cancers. |
Paclitaxel Story | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery of Paclitaxel Anti-cancer activity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unique mechanism of its anti-cancer activity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To date, 180 Paclitaxel Clinical Trials | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paclitaxel Supply Approaches | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New Resource -Taxus chinensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paclitaxel (Taxol) and Related Anticancer Drugs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Packing &loading | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACLITAXEL
10
gm – 500gm Packaged in a vacuum, water-repellent, anti-microbial, aluminum bag. Storage: Store in original package between 2° and 25°C (36° to 77°F). Retain in a container to protect from light.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early research using paclitaxel was limited by a restricted supply
due to several difficulties in obtaining the drug from the Taxus
brevifolia (Pacific yew). The concentration of the compound in
yew bark is low, and paclitaxel extraction is complex and expensive.
The Taxus brevifolia (Pacific yew) is a limited resource, it
grows very slow and is located in old-growth forests that are the
habitat of the endangered spotted owl.
As demand for paclitaxel increased, researchers have been exploring new resources to increase the availability of paclitaxel. BMS produces Paxlitaxel Injection (TaxolÒ ) via a semi-synthesis process from Taxus baccata (Europe Yew). There have been many research reports on the constitutions of othet yew tree species worldwide. Scientists in US, China, Japan, Taiwan and other countries have done detailed research on Taxus chinensisi (Chinese yew) as the new resource of paclitaxel. There are four Chinese yew species growing on the territory of China. Scientists proved that all of them contain paclitaxel at a similar level as the Taxus brevifolia. Scientists have isolated and identified 110 taxanes from Chinese yews, and 36 of them were new taxanes. in vitro and in vivo studies proved that paclitaxel has the strongest anti-cancer activity. Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises in cooperate with Chinese academic institutions developed a new production line to extract pure paclitaxel from planted 3-5 years young Taxus chinensis. With the large field of planted young Taxus chinensis, which contains paclitaxel as high as 0.015 - 0.02%, and the new manufacturing technology, China's Natural Paclitaxel has become the most reliable new resource of high quality natural paclitaxel with very competitive cost. Clinical trials in China since 1995 have proved the effectuveness and safety of Natural Paclitaxel Injection (which contains paclitaxel extracted from Taxus chinensis) in cancer treatment. The pure natural paclitaxel is ideal for the paharmaceutical manufacturers and research laboratories to use for developing new anti-cancer preparations,and new taxane derivatives |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This data is only for your information purposes and does not imply
guarantee for a certain application. Please note: We do not deliver the product Paclitaxel to private users! |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| If you need an indicative price to your country, please kindly advise the annual quantity needed, destination port and we will send you our soonest CNF(Cost + Freight) price. Your indication for a workable price level will sure speed up our fastest service for you | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
We really need to get
feed back from our customers in order to improve our performances. Best regards from SHENZHEN , China Mr. JEFFERY TSUI |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paclitaxel
is a cytotoxic anticancer drug, caution should be exercised in handling
paclitaxel. The use of gloves is recommended.
If paclitaxel solution contacts the skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. Following topical exposure, events have included tingling, burning and redness. If paclitaxel contacts mucous membranes, the membranes should be flushed thoroughly with water. Upon inhalation, dyspnea, chest pain, burning eyes, some throat and nausea have been reported. This product is for pharmaceutical manufacturers and research laboratories use only. It is not for the direct clinical administration. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Handling and Disposal: Procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.1-7 There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropriate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related Informations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacology of Paclitaxel and Docetaxel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CancerNet: Taxol and Related Anticancer Drugs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CancerNet: The New Taxoid -- Docetaxel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| If the above information doesn't cover |
contact us
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![]()
![]()